
01/8How to lower blood sugar levels quickly in case of an emergency
Diabetes is a metabolic health condition which impacts your body’s ability to regulate blood sugar levels (or glucose). In Type 1 diabetes, your body’s ability to produce insulin is impacted. The hormone insulin secreted by the pancreas helps the body to utilise the blood sugar as it moves the sugar from the blood into the cells to be used later. As a result, it prevents the blood sugar level in your body from getting too high. On the other hand, in Type 2 diabetes, your body is not able to make enough insulin to prevent the blood sugars from rising too high.
02/8The dangers of hyperglycemia
In any case, uncontrolled and untreated high blood sugar can lead to a host of medical problems and requires urgent medical treatment in a lot of cases. Hyperglycemia can also damage your eyes, kidney, nerves and heart, in the absence of timely treatment. It should be noted that careful monitoring of blood sugar levels through prescribed medications and lifestyle changes is extremely important.
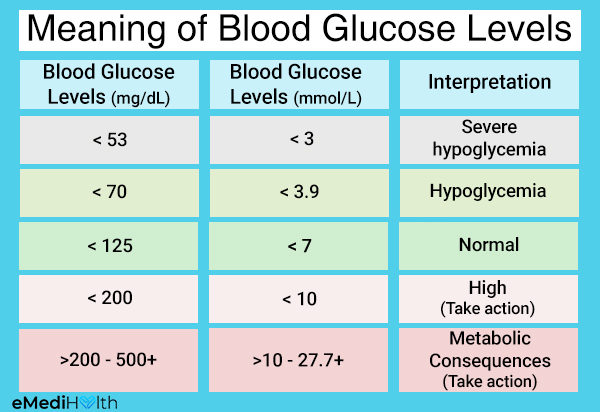
03/8What are increased levels of blood sugar
Hyperglycemia is the condition when your body is not producing enough insulin and your blood glucose levels are higher than normal. Blood sugar levels less than 140 milligrams per deciliter is considered normal. However, if your blood sugar is higher than 130 milligrams per deciliter before having a meal and more than 180 milligrams per deciliter two hours after eating, it is considered abnormally high levels of blood sugar. Some of the most common symptoms of high blood sugar include:
1.Increased thirst
2.Frequent urination
3. Blurred vision
04/8What should you do if your blood sugar levels shoot up
When your blood sugar levels get too high, it can cause serious complications if not treated on time. If you are experiencing hyperglycemia or high blood sugar, it is important to ensure that it doesn’t go too high and the levels come down to normal quickly.
05/8A dose of insulin
One of the quickest ways to tackle hyperglycemia is to take insulin. It is important to ensure that you have a word with your doctor before dosing yourself with insulin to lower down your blood sugar levels. Make sure you speak to your medical care advisor about the dose of a rapid-acting insulin and check your blood sugar after 15-30 minutes again.
06/8Try some light exercises like walking, spot jogging
Even though light exercises do help in lower the blood sugar levels in the body for most diabetic patients, you still need to tread with caution. If your blood sugar level has reached an alarmingly high level (more than 240 milligrams per deciliter) and ketones are detected in your urine, steer clear of exercising as it may further raise your blood sugar. People with type 1 diabetes especially should not exercise if they are witnessing a spike in their blood sugar levels. On the other hand, exercise can bring down your blood sugar levels when done regularly over a period of time and is crucial in managing diabetes.
07/8Drink more water
Several reports state that drinking more water can help your body flush out the excess sugar out through urine. However, more research is needed to support this statement.
08/8When is high blood sugar a medical emergency?
Extremely high levels of blood sugar that remain untreated for a long time may lead to diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA). In diabetic ketoacidosis, your blood sugar levels shoot up really high and lead to the build-up of ketones in your body. This serious medical condition can lead to diabetic coma or even death. Some of the warning signs of DKA include:
1.Shortness of breath
2.Fruity breath
3.Nausea and vomiting
4.A very dry mouth
Remember, DKA should be treated as a medical emergency and you should consult a doctor as soon as possible.


No comments:
Post a Comment